Optic Nerve
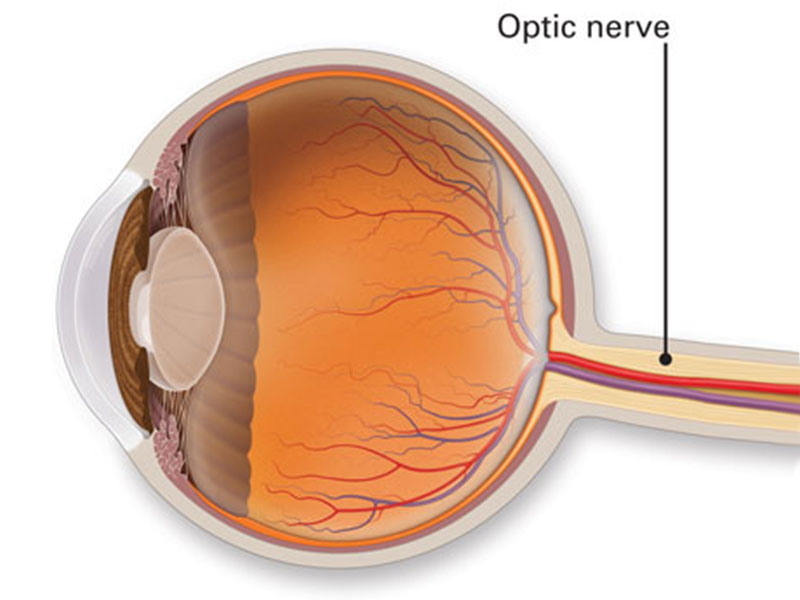
The optic nerve is located in back of the eye. It is also known as the second cranial nerve or cranial nerve II. It is the second of many pairs of the cranial nerves. The main function of the optic nerve is to transfer visual information from retina to the vision centers of brain by electrical impulses.
The optic nerve is made of nerve cells or ganglionic cells. It consists of over 1 million nerve fibers. Blind spot is absent of photosensitive (light-sensitive), or photoreceptor cells.
The optic nerve will transmit all the visual information that includes brightness perception, color perception & contrast (visual acuity). It also conducts the visual impulses which are accountable for 2 important & main neurological reflexes: The light reflex & the accommodation reflex. The light reflex refers to the constriction of both the pupils which occurs when the light is shone into either eye. The accommodation reflex refers to the swelling of lens of the eye which occurs when a person looks at a near object while reading (lens adjusts to near vision).
Based on this anatomy, the optic nerve can be divided into 4 parts:
- The optic head (where it begins in eyeball (globe) along with the fibers from retina)
- Orbital part (which is the part of the orbit).
- Intrancanalicular part (which is the part within a bony canal called the optic canal)
- Intracranial part (part within cranial cavity, which ends at optic chiasma)
Glaucoma is one of the major eye diseases that affects the optic nerve. Glaucoma is caused by a high intraocular pressure, or high pressure in the fluid which is inside the eye (vitreous fluid). This high pressure will compress the optic nerve & cause the cells to die. It is referred as the atrophy of the optic nerve.
Even though the optic nerve is a part of the eye, it is considered as part of the central nervous system.









 I am Nimitha, before Lasik, I am very difficult to see and difficult to handle contact lens and specs. After the lasik treatment I am very relaxed.
I am Nimitha, before Lasik, I am very difficult to see and difficult to handle contact lens and specs. After the lasik treatment I am very relaxed. 